Foodborne Illness
Foodborne Illness
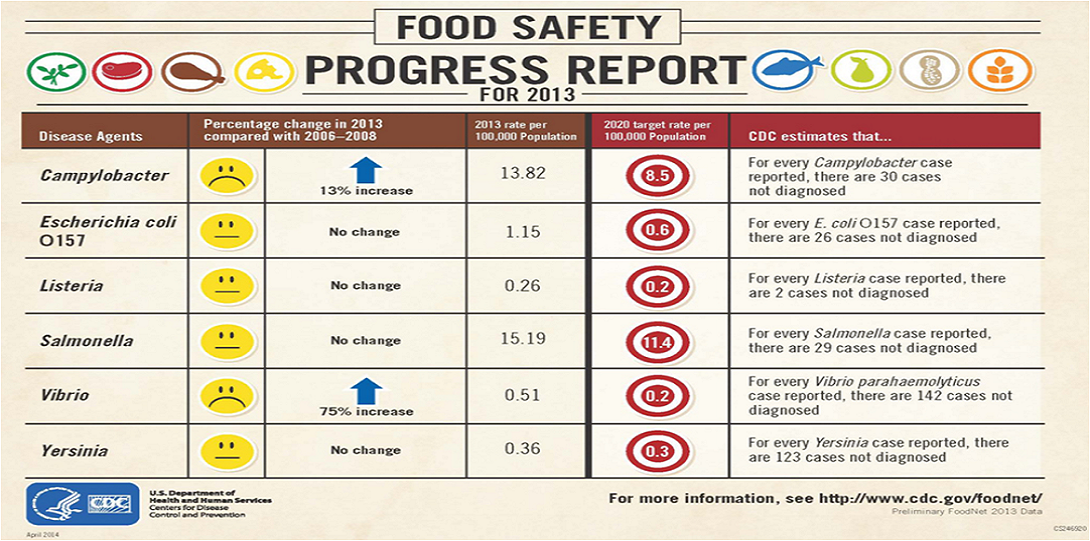
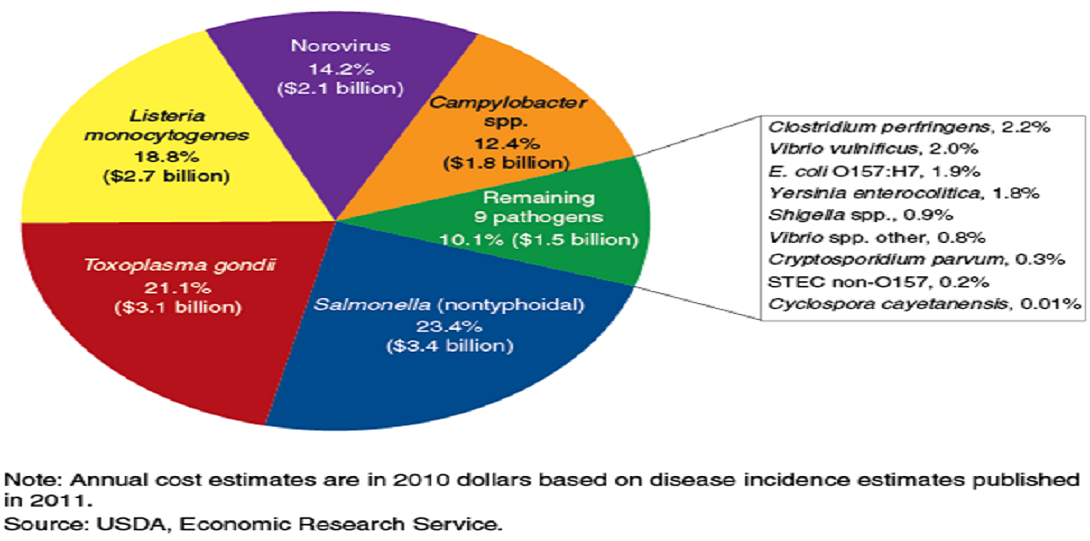
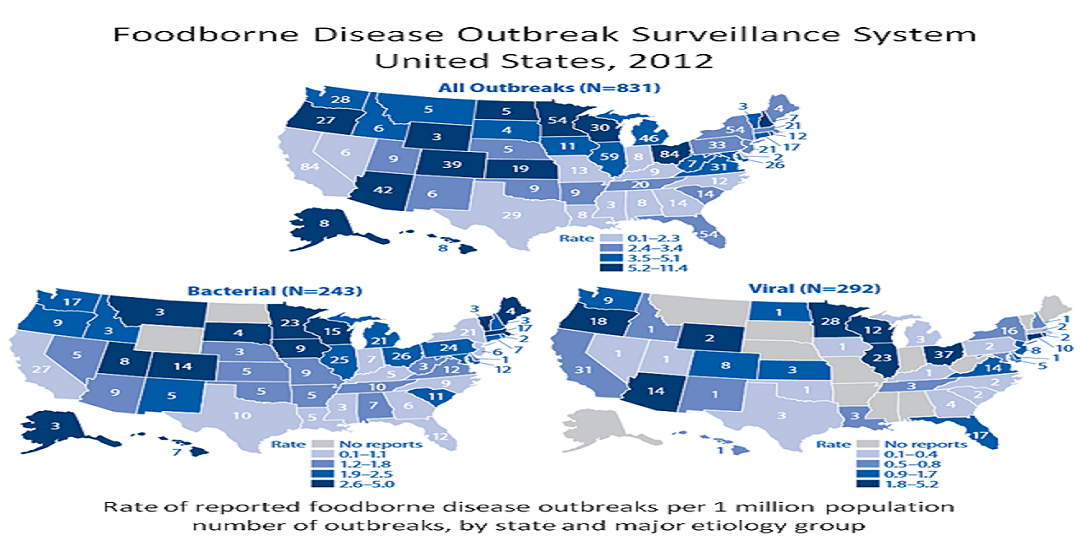
Foodborne illness (sometimes called “foodborne disease,” “foodborne infection,” or “food poisoning”) is a common, costly—yet preventable—public health problem. CDC estimates that each year roughly 1 in 6 Americans (or 48 million people) get sick, 128,000 are hospitalized, and 3,000 die of foodborne diseases.
5 Most common foodborne illness risk factors
1. Improper holding time and temperatures
2. Poor personal hygiene
3. Inadequate cooking
4. Contaminated equipment
5. Food from unsafe source
| Germs | Food |
|---|---|
| Campylobacter | Poultry |
| E.Coli | Ground Beef |
| Listeria | Deli meats, Unpasteurized diary |
| Salmonella | Eggs, Poultry, Meat |
| Vibrio | Raw oysters |
| Norovius | Many foods (sandwiches, salads) |